What Is An Economic Impact Analysis (EIA)?
Economic Impact Analysis (EIA) is a powerful technique used to trace spending through an economy, measuring the cumulative effects of that spending. This process, also known as Input-Output analysis, provides valuable insights into how economic activity ripple through industries, households, and government entities. IMPLAN is a leading economic impact analysis software that democratizes this technique, making it accessible to business, policymakers, and researchers alike.
Want to dive deeper? Check out our guides: Mastering Economic Analysis or The Economic Developer’s Guide to Impact Analysis.
What Is An Economic Impact Analysis (EIA)?
Economic Impact Analysis (EIA) is a powerful technique used to trace spending through an economy, measuring the cumulative effects of that spending. This process, also known as Input-Output analysis, provides valuable insights into how economic activity ripple through industries, households, and government entities. IMPLAN is a leading economic impact analysis software that democratizes this technique, making it accessible to business, policymakers, and researchers alike.
Want to dive deeper? Check out our guides: Mastering Economic Analysis or The Economic Developer’s Guide to Impact Analysis.
What does an economic impact analysis measure?
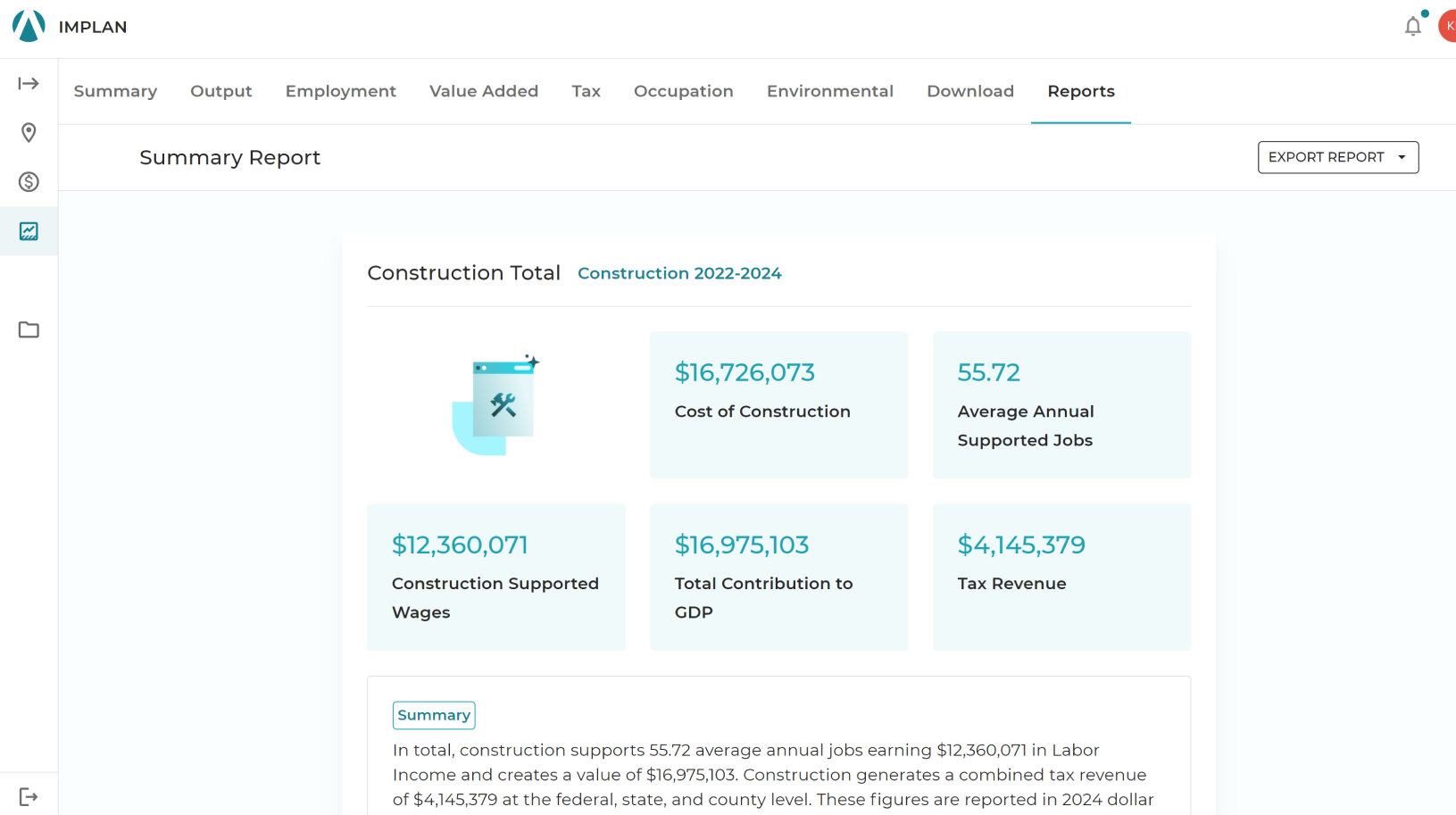
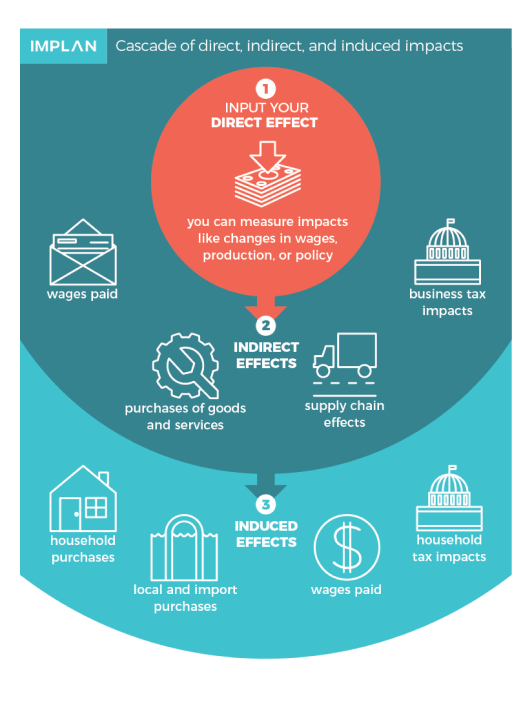
An EIA measures three core components of economic activity:
- Direct Effects: These are the initial changes in the economy caused by an event, investment, or activity. For example, when a company builds a factory, the direct effects include the construction expenditures and the jobs created.
- Indirect Effects: Indirect effects result from the supply chain activity generated by the direct effects. Using the factory example, this includes the suppliers providing construction materials, machinery, and other inputs.
- Induced Effects: Induced effects capture the additional economic activity driven by spending from wages earned by workers in the direct and indirect stages. Employees’ spending on goods, services, and housing contributes to these effects.
Explore real-world examples through our case studies:
How to conduct an economic impact analysis
Conducting an EIA requires careful planning and accurate data. Here are the basic steps:
- Gather the Necessary Data
- Spending amounts
- Employment figures
- Industry codes
- Understand Key Terms
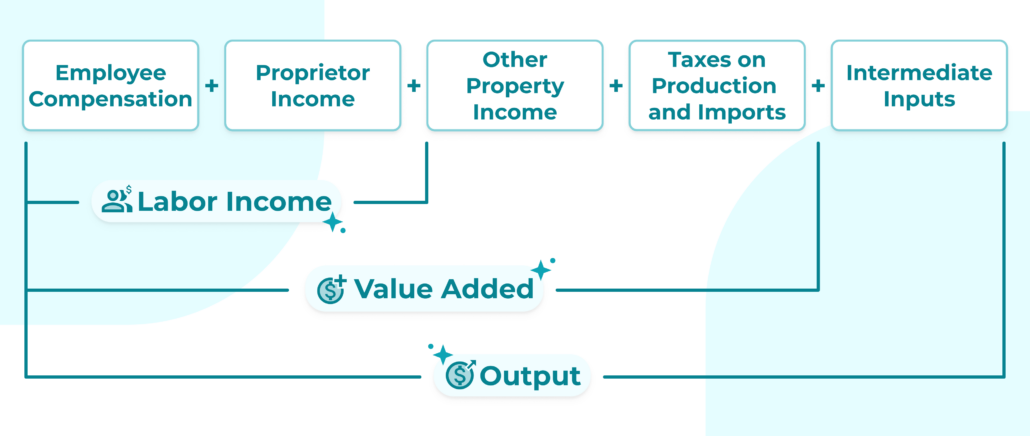
- Input-Output Analysis (IO): A quantitative method for analyzing relationships between industries within an economy.
- Multipliers: Metrics that measure how initial spending translates into additional economic activity.
For a step-by-step breakdown, check out our How-to Guide or browse related blog posts.
Economic Impact analysis by IMPLAN
IMPLAN simplifies economic impact analysis, offering:
- Comprehensive Data: Access to detailed industry, regional, and demographic data.
- Customizable Scenarios: Tailor analyses to specific projects, policies, or regions.
- User-Friendly Tools: Intuitive platform with powerful visualization and reporting capabilities.
Whether you’re conducting a feasibility study, evaluating policy impacts, or exploring new markets, IMPLAN empowers you to make data-driven decisions with confidence.
Interested in learning more? See IMPLAN in action or book your demo with us today to explore how IMPLAN can enhance your economic analyses.
- Visualize Economic Impacts: Create detailed visualizations that highlight the effects of various economic scenarios, making it easier to communicate findings to stakeholders.
- Support Policy Advocacy: Equip yourself with robust evidence to advocate for policies that benefit your community or organization. Present data-backed arguments that resonate with decision-makers.
- Enhance Project Planning: Use our advanced modeling capabilities to assess the economic implications of potential projects, ensuring you make decisions that drive sustainable growth.
- Collaborate with Experts: Join a network of professionals who leverage IMPLAN for insightful economic analysis. Share ideas, best practices, and learn from others in the field.
- Stay Ahead of Trends: With access to up-to-date data and resources, IMPLAN helps you stay informed about economic trends that could impact your industry or region.



